Global advances in tomato virome research: current status and the impact of high-throughput sequencing
Rivarez MPS, Vučurović A, Mehle N, Ravnikar M and Kutnjak D (2021) Global Advances in Tomato Virome Research: Current Status and the Impact of High-Throughput Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 12:671925. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.671925 In this review paper we have collected the existing knowledge about the viruses infecting tomato, focusing on the viruses that caused important economic damage in tomato production in a past decade. We have also addressed how high-throughput sequencing technologies have contributed to discovery of novel viruses infecting tomato and evaluated the extent of post-discovery characterisation studies for such viruses.
- 26 January 2023
- Yolanda Hernando Saiz
- < back to blog index
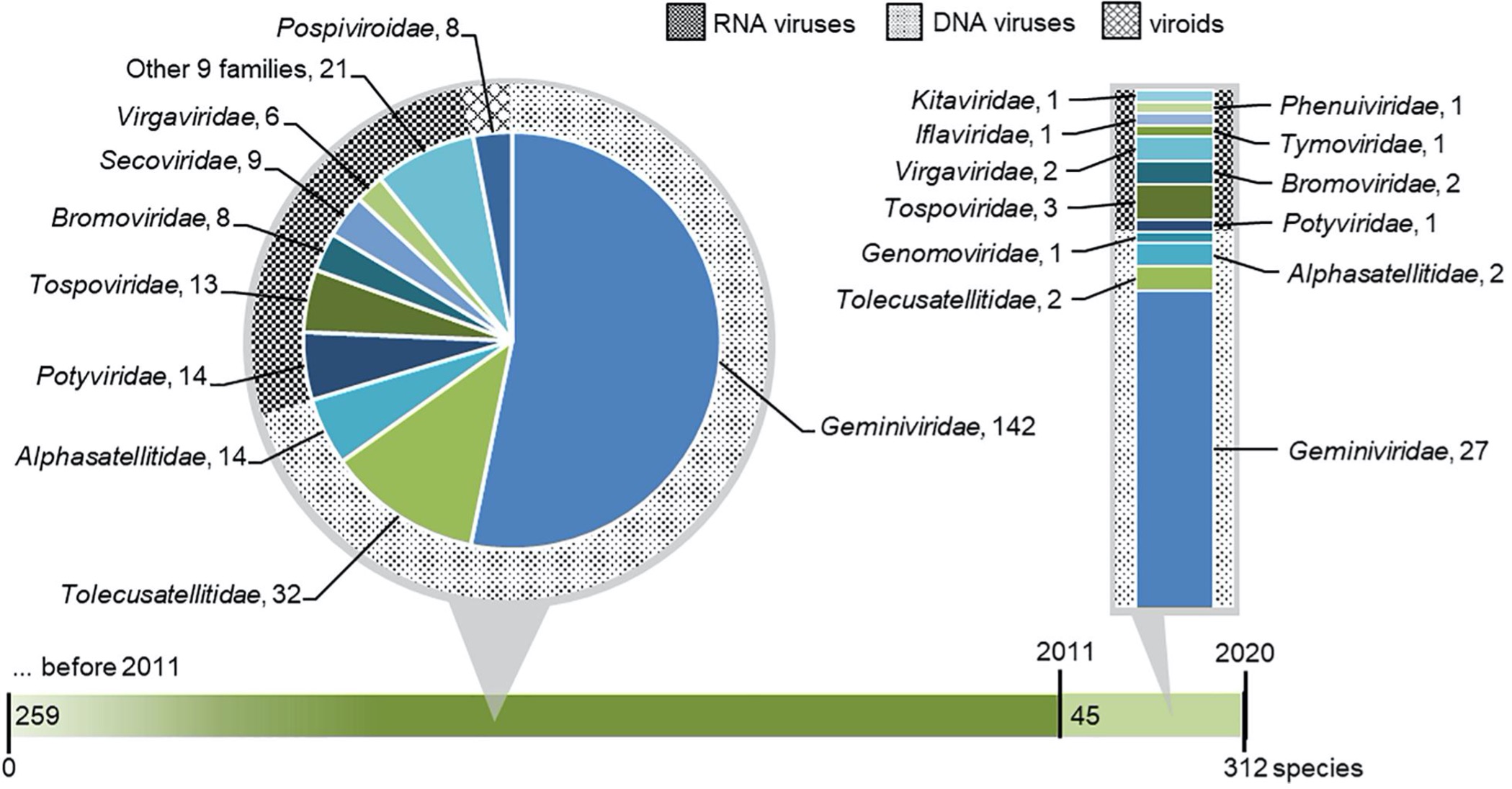
Viruses cause a big fraction of economically important diseases in major crops, including tomato. In the past decade (2011–2020) 45 novel viral species were identified in tomato, 14 of which were discovered using high-throughput sequencing (HTS). We observed that the rate of tomato virus discovery is accelerating in the past few years due to the use of HTS. However, the extent of the post-discovery characterization of viruses is lagging behind and is greater for economically devastating viruses, such as the recently emerged tomato brown rugose fruit virus. The review of databases and literature revealed at least 312 virus, satellite virus, or viroid species associated with tomato, which is likely the highest number recorded for any plant. Increasing knowledge on tomato virome and employment of HTS to also study viromes of surrounding wild plants and environmental samples are bringing new insights into the understanding of epidemiology and ecology of tomato-infecting viruses.
< back to blog index
Recent posts
- Carrot populations in France and Spain host a complex virome rich in previously uncharacterized viruses
- VIROME ANALYSIS OF IRRIGATION WATER SOURCES PROVIDES EXTENSIVE INSIGHTS INTO THE DIVERSITY AND DISTRIBUTION OF PLANT VIRUSES IN AGROECOSYSTEMS
- Round table: https://youtu.be/XPYOCrXqqOQ
- Managing the deluge of newly discovered plant viruses and viroids: an optimized scientific and regulatory framework for their characterization and risk analysis
- A new flavi-like virus identified in populations of wild carrot
- Tomato brown rugose fruit virus in aqueous environments – survival and significance of water-mediated transmission
- First report of carrot torrado virus 1 (CaTV1) naturally infecting carrots in Spain
- VirHunter: A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Novel RNA Viruses in Plant Sequencing Data
- Diversity of polerovirus-associated RNAs in the virome of wild carrots
- First report of Apium virus Y in wild carrot (Daucus carota ssp. carota) in Spain
- Tobamoviruses show broad host ranges and little genetic diversity among four habitat types of a heterogeneous ecosystem.
- Metagenomics show high spatiotemporal virus diversity and ecological compartmentalisation: virus infections of melon, Cucumis melo, crops and adjacent wild communities
- Web-based roundtable: Adoption and impact of high throughput sequencing in plant health: Seed testing, surveillance and certification
- Identification of two novel putative satellite RNAs with hammerhead structures in the virome of French and Spanish carrot samples
- Diversity and pathobiology of an Ilarvirus unexpectedly detected in diverse plants and global sequencing data
- First Report of Ranunculus White Mottle Ophiovirus in Slovenia in Pepper with Yellow Leaf Curling Symptom and in Tomato
- In-depth study of tomato and weed viromes reveals undiscovered plant virus diversity in an agroecosystem
- THE EXPANDING MENAGERIE OF PRUNUS-INFECTING LUTEOVIRUSES
- Molecular characterization of a new Prunus-infecting cheravirus and complete genome sequence of stocky prune virus
- Genetic differentiation and migration fluxes of viruses from melon crops and crop edge weeds
- Global advances in tomato virome research: current status and the impact of high-throughput sequencing
- Cont-ID: Detection of samples cross-contamination in viral metagenomic data
- Validation of high throughput sequencing as virus indexing test for Musa germplasm: performance criteria evaluation and contamination monitoring using an alien control
- HIGH THROUGHPUT SEQUENCING TECHNOLOGIES COMPLEMENTED BY GROWER’S PERCEPTION HIGHLIGHT THE IMPACT OF TOMATO VIROME IN DIVERSIFIED VEGETABLE FARMS
- BIOLOGICAL AND GENETIC CHARACTERIZATION OF PHYSOSTEGIA CHLOROTIC MOTTLE VIRUS IN EUROPE BASED ON HOST RANGE, LOCATION, AND TIME
- Risk perception associated with an emerging agri-food risk in Europe: plant viruses in agriculture
- First reports of Apple luteovirus 1, Apple rubodvirus 1 and Apple hammerhead viroid infecting apples in Belgium
- Evaluation of Methods and Processing for Robust Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater
- Importance of associated weeds and cropping systems in shaping the viromes of horticultural crops. Ayoub Maachi PhD Thesis
- Use of high throughput sequencing and two RNA input methods to identify viruses infecting tomato crops.
- Complete genome sequence of malva-associated soymovirus 1: a novel virus infecting common mallow
- Cohombrillo-associated virus: a novel virus infecting Ecballium elaterium plants
- Known and new viruses identified in the virome of crops scanned by INEXTVIR
- Scanning the virome of Prunus : Identification and characterization of novel luteoviruses and Secoviridae members
- Complete genome sequence of almond luteovirus 1, a novel luteovirus species infecting almond
- INEXTVIR Mid-Term Check + Network Meeting 2 + School 2