Tomato brown rugose fruit virus in aqueous environments – survival and significance of water-mediated transmission
NATAŠA MEHLE, KATARINA BAČNIK, IRENA BAJDE, JAKOB BRODARIČ, ADRIAN FOX, ION GUTIÉRREZ-AGUIRRE, MIHA KITEK, DENIS KUTNJAK, YUE LIN LOH, OLIVERA MAKSIMOVIĆ CARVALHO FERREIRA, MAJA RAVNIKAR, ELISE VOGEL, CHRISTINE VOS, ANA VUČUROVIĆ. DOI.ORG/10.3389/FPLS.2023.1187920In this study we aimed towards filling some of the knowledge gaps in the epidemiology and diagnosis of ToBRFV, by studying the virus survival in water, the detection of the virus in environmental irrigation waters and the role of water-mediated transmission on its epidemiology.
- 02 July 2023
- Yolanda Hernando Saiz
- < back to blog index
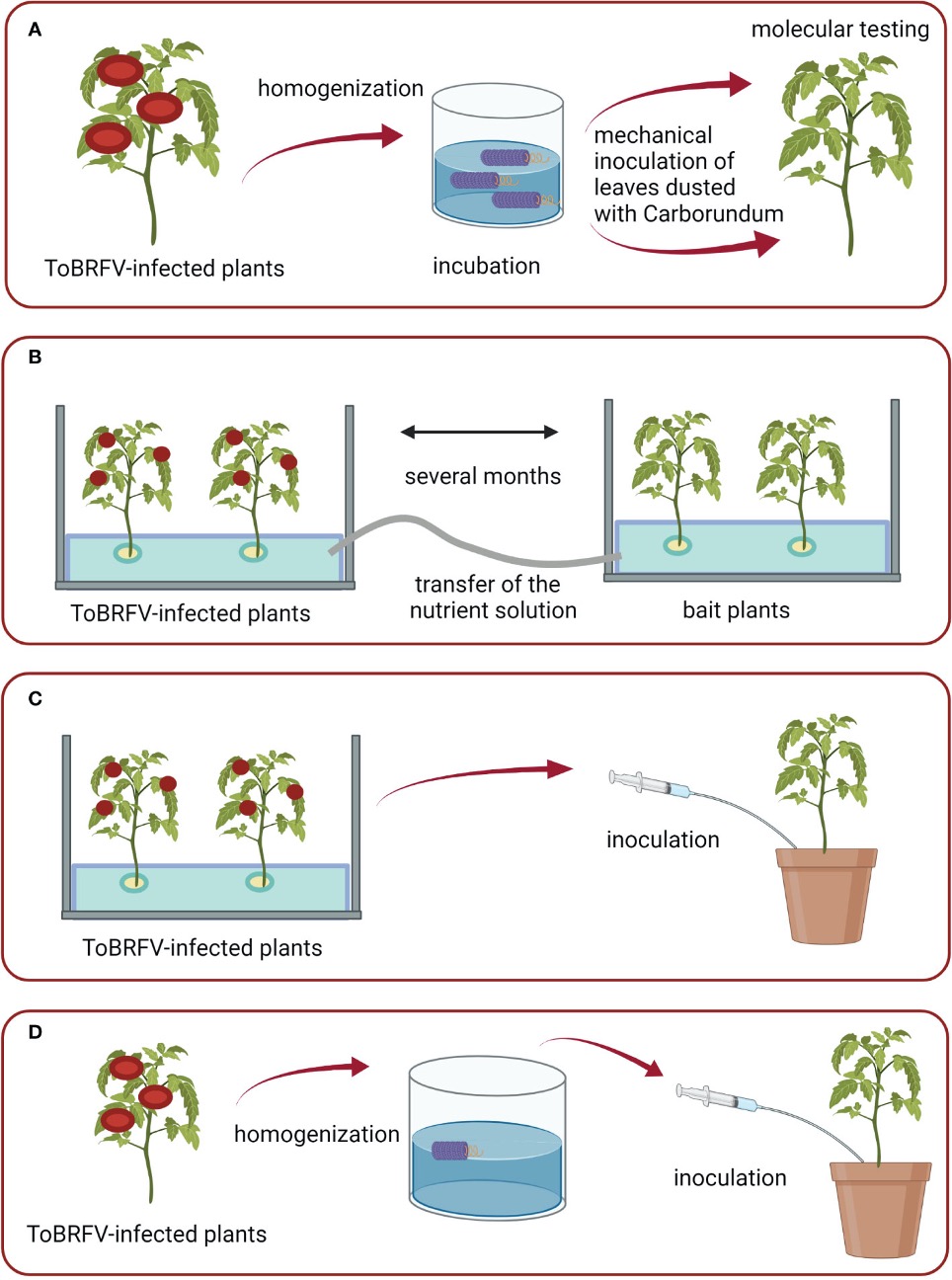
Tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) has recently emerged as a major disease of tomatoes and peppers. ToBRFV is a seed- and contact-transmitted virus. In Slovenia, ToBRFV RNA was detected in samples of wastewater, river, and water used to irrigate plants. Even though the source of detected RNA could not be clearly established, this raised the question of the significance of the detection of ToBRFV in water samples and experimental studies were performed to address this question. The data presented here confirm that the release of virus particles from the roots of infected plants is a source of infectious ToBRFV particles in water and that the virus can remain infective up to four weeks in water stored at room temperature, while its RNA can be detected for much longer. These data also indicate that irrigation with ToBRFV-contaminated water can lead to plant infection. In addition, it has been shown that ToBRFV circulated in drain water in commercial tomato greenhouses from other European countries and that an outbreak of ToBRFV can be detected by regular monitoring of drain water. A simple method for concentrating ToBRFV from water samples and a comparison of the sensitivity of different methods, including the determination of the highest ToBRFV dilution still capable of infecting test plants, were also investigated. The results of our studies fill the knowledge gaps in the epidemiology and diagnosis of ToBRFV, by studying the role of water-mediated transmission, and provide a reliable risk assessment to identify critical points for monitoring and control.
< back to blog index
Recent posts
- Carrot populations in France and Spain host a complex virome rich in previously uncharacterized viruses
- VIROME ANALYSIS OF IRRIGATION WATER SOURCES PROVIDES EXTENSIVE INSIGHTS INTO THE DIVERSITY AND DISTRIBUTION OF PLANT VIRUSES IN AGROECOSYSTEMS
- Round table: https://youtu.be/XPYOCrXqqOQ
- Managing the deluge of newly discovered plant viruses and viroids: an optimized scientific and regulatory framework for their characterization and risk analysis
- A new flavi-like virus identified in populations of wild carrot
- Tomato brown rugose fruit virus in aqueous environments – survival and significance of water-mediated transmission
- First report of carrot torrado virus 1 (CaTV1) naturally infecting carrots in Spain
- VirHunter: A Deep Learning-Based Method for Detection of Novel RNA Viruses in Plant Sequencing Data
- Diversity of polerovirus-associated RNAs in the virome of wild carrots
- First report of Apium virus Y in wild carrot (Daucus carota ssp. carota) in Spain
- Tobamoviruses show broad host ranges and little genetic diversity among four habitat types of a heterogeneous ecosystem.
- Metagenomics show high spatiotemporal virus diversity and ecological compartmentalisation: virus infections of melon, Cucumis melo, crops and adjacent wild communities
- Web-based roundtable: Adoption and impact of high throughput sequencing in plant health: Seed testing, surveillance and certification
- Identification of two novel putative satellite RNAs with hammerhead structures in the virome of French and Spanish carrot samples
- Diversity and pathobiology of an Ilarvirus unexpectedly detected in diverse plants and global sequencing data
- First Report of Ranunculus White Mottle Ophiovirus in Slovenia in Pepper with Yellow Leaf Curling Symptom and in Tomato
- In-depth study of tomato and weed viromes reveals undiscovered plant virus diversity in an agroecosystem
- THE EXPANDING MENAGERIE OF PRUNUS-INFECTING LUTEOVIRUSES
- Molecular characterization of a new Prunus-infecting cheravirus and complete genome sequence of stocky prune virus
- Genetic differentiation and migration fluxes of viruses from melon crops and crop edge weeds
- Global advances in tomato virome research: current status and the impact of high-throughput sequencing
- Cont-ID: Detection of samples cross-contamination in viral metagenomic data
- Validation of high throughput sequencing as virus indexing test for Musa germplasm: performance criteria evaluation and contamination monitoring using an alien control
- HIGH THROUGHPUT SEQUENCING TECHNOLOGIES COMPLEMENTED BY GROWER’S PERCEPTION HIGHLIGHT THE IMPACT OF TOMATO VIROME IN DIVERSIFIED VEGETABLE FARMS
- BIOLOGICAL AND GENETIC CHARACTERIZATION OF PHYSOSTEGIA CHLOROTIC MOTTLE VIRUS IN EUROPE BASED ON HOST RANGE, LOCATION, AND TIME
- Risk perception associated with an emerging agri-food risk in Europe: plant viruses in agriculture
- First reports of Apple luteovirus 1, Apple rubodvirus 1 and Apple hammerhead viroid infecting apples in Belgium
- Evaluation of Methods and Processing for Robust Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater
- Importance of associated weeds and cropping systems in shaping the viromes of horticultural crops. Ayoub Maachi PhD Thesis
- Use of high throughput sequencing and two RNA input methods to identify viruses infecting tomato crops.
- Complete genome sequence of malva-associated soymovirus 1: a novel virus infecting common mallow
- Cohombrillo-associated virus: a novel virus infecting Ecballium elaterium plants
- Known and new viruses identified in the virome of crops scanned by INEXTVIR
- Scanning the virome of Prunus : Identification and characterization of novel luteoviruses and Secoviridae members
- Complete genome sequence of almond luteovirus 1, a novel luteovirus species infecting almond
- INEXTVIR Mid-Term Check + Network Meeting 2 + School 2